Chapter 1: What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a NoSQL database.
A NoSQL Database is a database that is structured and can be accessed in a different way to SQL databases, it doesn’t use a legacy approach of related tables of data, not in rows and columns.
- The data in MongoDB DB is stored in Documents.
- Documents are stored in Collections.

What is a Document?
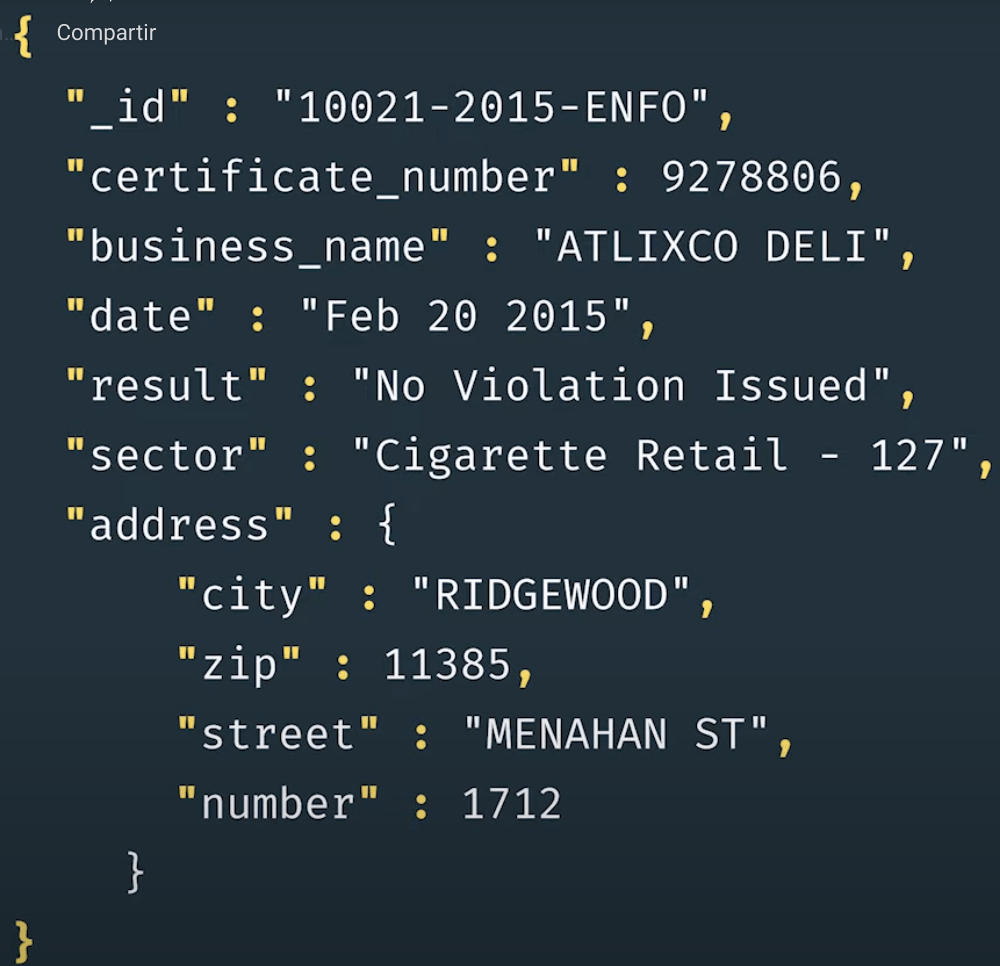
Is a way to organize and store data as a set of field-value pairs.
Field - a unique identifier for a data point.
Value - data related to a given identifier.
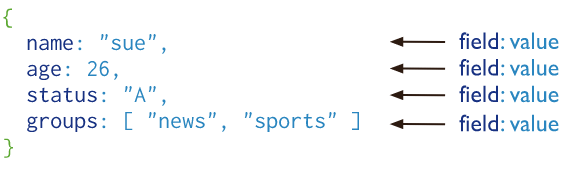
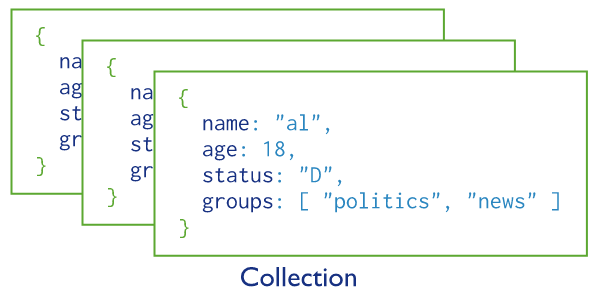
What is a Collection?
An organized store of documents in MongoDB, usually with common fields between documents.
There can be many collections per-database and many documents per collection.
What is MongoDB Atlas?
Atlas is a cloud service that provides a fully managed database built for a range-wide of applications with MongoDB at its core.
It allows you to visualize, export, and more.
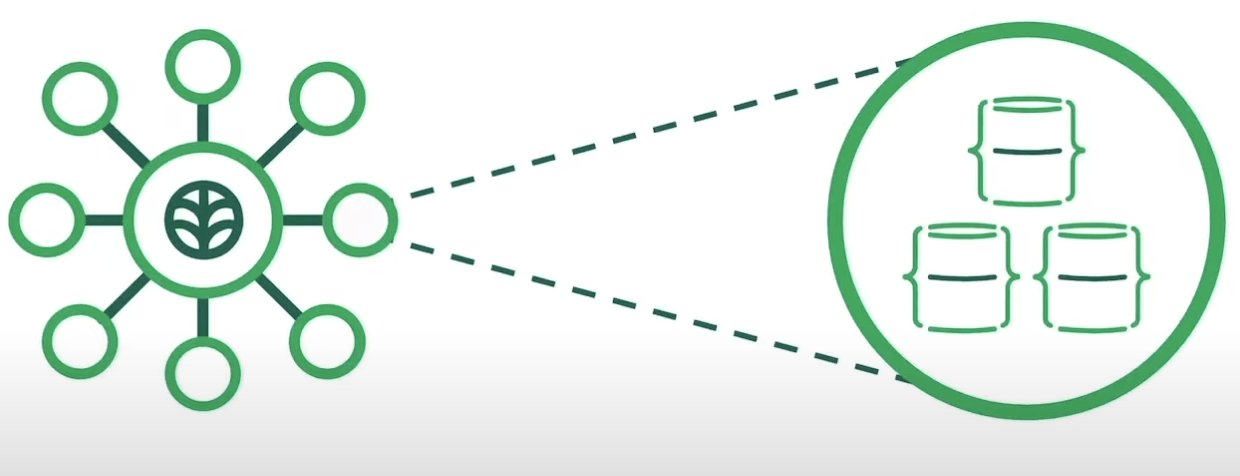
Cluster Deployment
Atlas users can deploy Clusters.
Cluster - group of servers that store your data.
These Clusters are configured in Replica Set.
Replica Set - a few connected MongoDB instances that store the same data to ensure that if something happens to one of the machines the data will remain intact. Comes from the word replicate - to copy something.
The major difference between a replica set and a cluster is:
- A replica set copies the data set as a whole.
- A cluster distributes the workload and stores pieces of data (shards) across multiple servers.
MongoDB allows users to combine these two functionalities by creating a sharded cluster, where each shard is replicated to a secondary server in order to provide high data availability and redundancy.
Instance - a single machine locally or in the cloud, running certain software, in our case it is the MongoDB database.
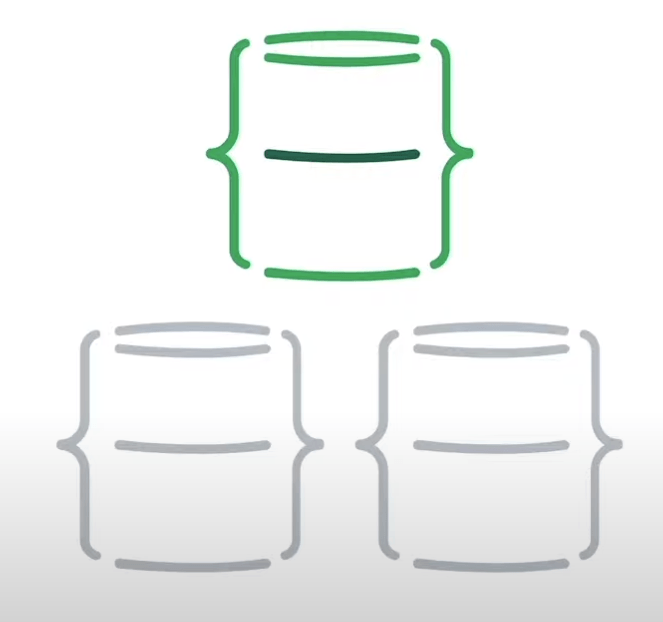
This setup ensures that if something happened to one of the machines in the Replica Set, the data will remain intact and available for use by the application by the remaining working member.
Every time that you make a change to a document or collection, redundant copies of that data are stored within the replica set.
It means a copy of that document will exist on every machine in the Replica Set.
ℹ️ To go deeper about ReplicaSet and Clusters, you can check this answer in StackOverflow: What is the difference between a cluster and a replica set in MongoDB atlas?
Services
- Managed cluster creation
- Run and maintain database deployment
- Use the cloud provider of your choice
- Experiment with new tools and features
Pricing

Some free tier features

Useful Links:
Chapter 2: Importing, Exporting, and Querying Data
How documents are represented?
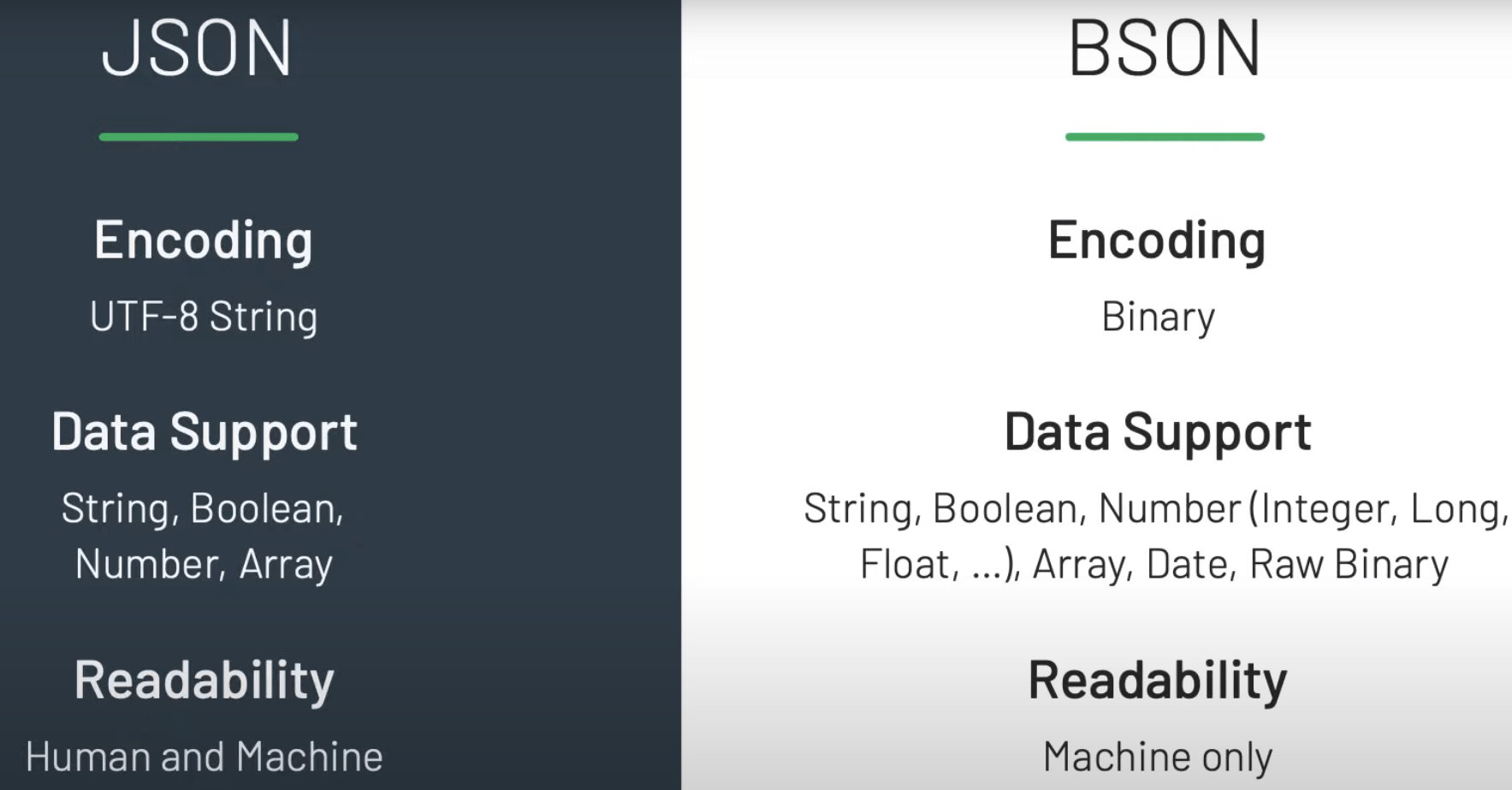
Documents are saved as BSON which is a binary representation of JSON.
JSON is:
- User friendly
- Readable
- Familiar
Cons of JSON:
- Text-based
- Space Consuming
- Limited number of data types.
BSON is optimized for:
- Speed
- Space
- Flexibility
- High performance
- General-purpose focus
The additional types in BSON allow for easing communication.
MongoDB stores data in BSON internally and over the network, but this doesn’t mean you can’t think of MongoDB as a JSON Database.
Anything you can represent in JSON can also be stored in MongoDB.
We can retrieve and store data as JSON. Actually, with native SDK always use JSON, we don’t think about BSON, it’s just an internal feature that in our day-to-day we never think of.
Optional reading:
Importing and Exporting Data
Data is Stored in BSON but Viewed in JSON
BSON is great but isn’t human-readable
To learn more about other mongoimport supported formats check out this documentation page.
SRV connection string - a specific format used to establish a connection between your application and a MongoDB instance. Click here to learn more.
Code used in this lecture:
mongodump --uri "mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies"
mongoexport --uri="mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --collection=sales --out=sales.json
mongorestore --uri "mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --drop dump
mongoimport --uri="mongodb+srv://<your username>:<your password>@<your cluster>.mongodb.net/sample_supplies" --drop sales.json
Terminal Commands

Exporting

Importing

Data Explorer
mongosh allows you to interact with your MongoDB instance without using a Graphical User Interface

Chapter 3: Creating and Manipulating Documents
Inserting New Documents - ObjectId
Every document must have a unique _id value.
Optional Reading
If you want to read more about the ObjectId data type, and the ObjectId() function, which generates ObjectId values, check out this excellent documentation page.
Every document can have a different structure, nothing prevents you from doing this. Either is a good practice to know how to organize your data.
The default value of _id field is ObjectId() unless otherwise is specified.
Idential documents can exist in the same collection as long as their _id values are different.
MongoDB has schema validation functionality allow you to enforce document structure.
Inserting New Documents - insert() order
Insert in order, which means if something fails, it will fail and will not continue with the next item.
db.inspections.insert([{ "_id": 1, "test": 1 },{ "_id": 1, "test": 2 },{ "_id": 3, "test": 3 }])We can avoid this behaviour by adding the option { ordered: false
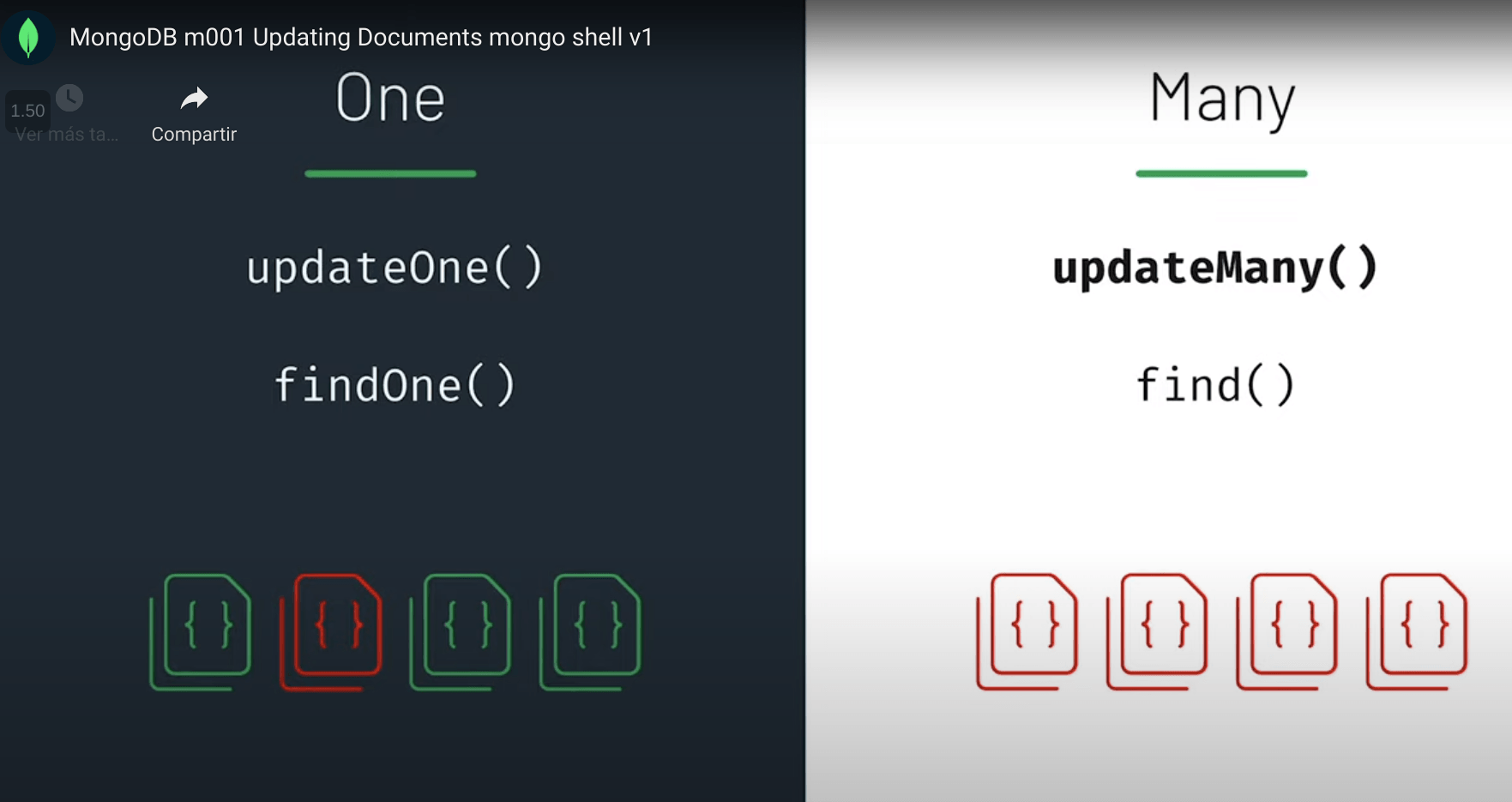
db.inspections.insert([{ "_id": 1, "test": 1 },{ "_id": 1, "test": 2 }, { "_id": 3, "test": 3 }], { ordered: false } )Updating Documents - mongo shell
Deleting Documents and Collections
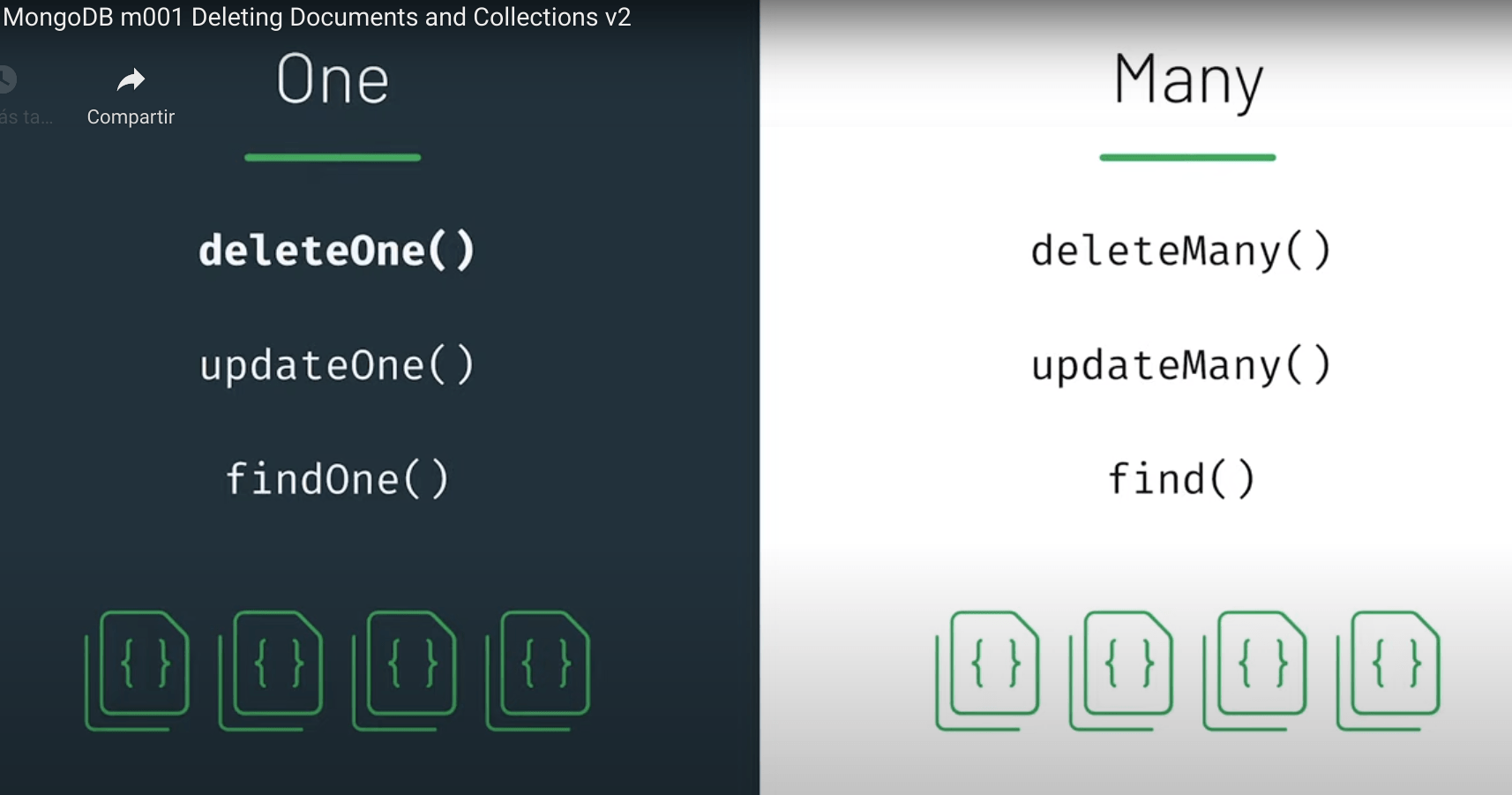
We can delete a collection by doing:
db.collection_name.drop()When we delete all collections from a database, the database will be removed as well.
Update operators
Example: $inc $set $unset
Chapter 4: Advanced CRUD Operations
Query Operators - Comparison
Query operators provide additional ways to locate data within the database
Comparison operators specifically allow us to find data within a certain range.

If a comparison operator is not specified, $eq is used as default operator.
Check the list of comparison operators here.
Query Operators - Logic

Structure:

And
And is implicit:

Here, and is implicit.


Expressive Query Operator
$ denotes the use of an operator
$ addresses the field value



Array Operators
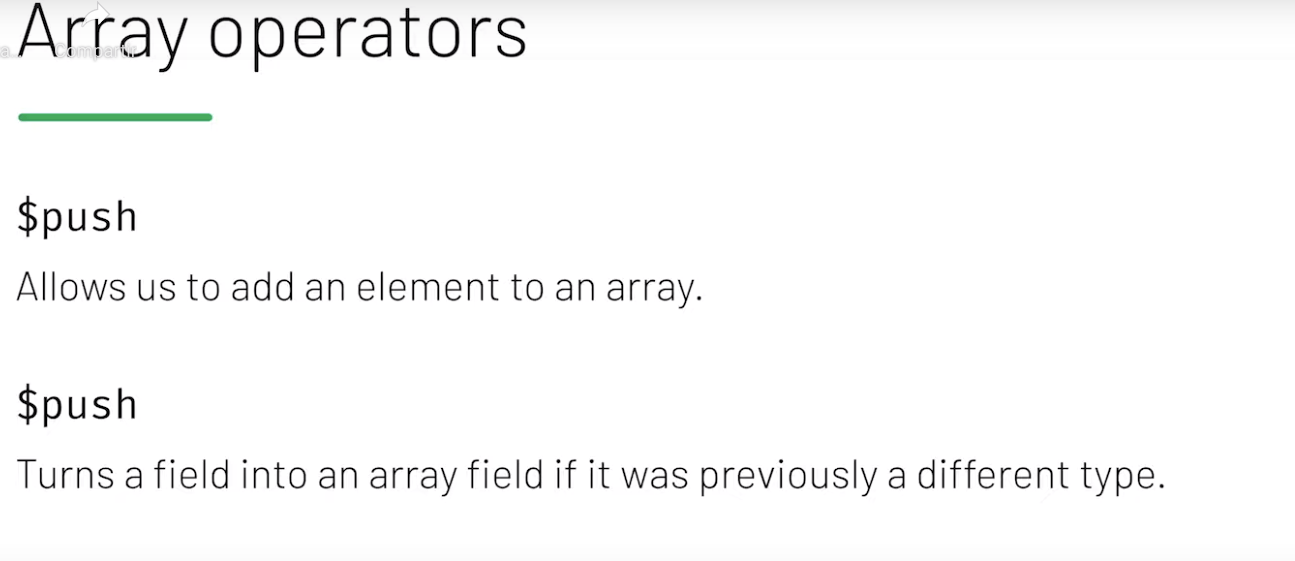

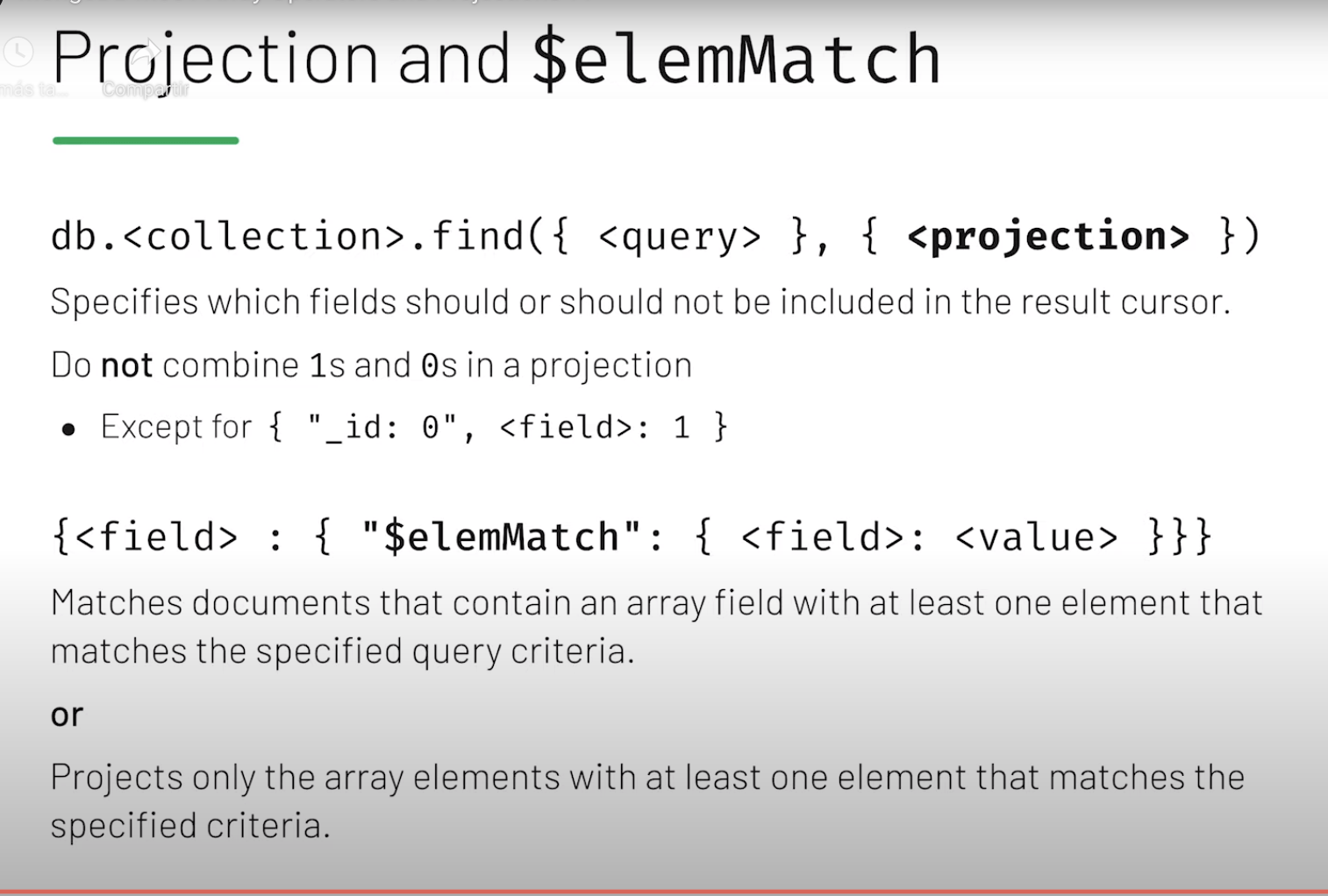
Array Operators and Projection
Chapter 5: Indexing and Aggregation Pipeline
Another way to create queries.
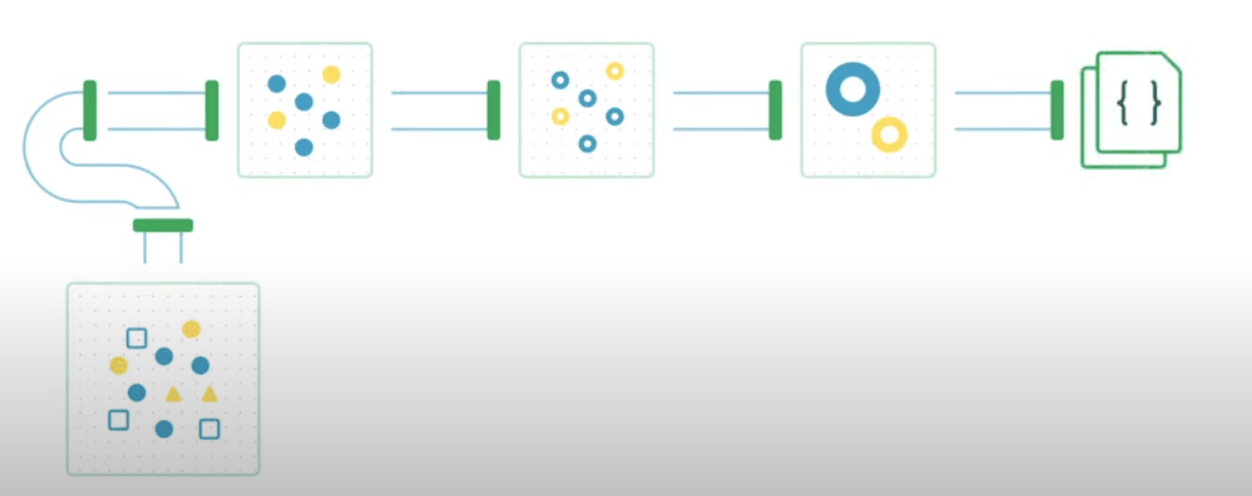
Get into the bus at 1st St. then
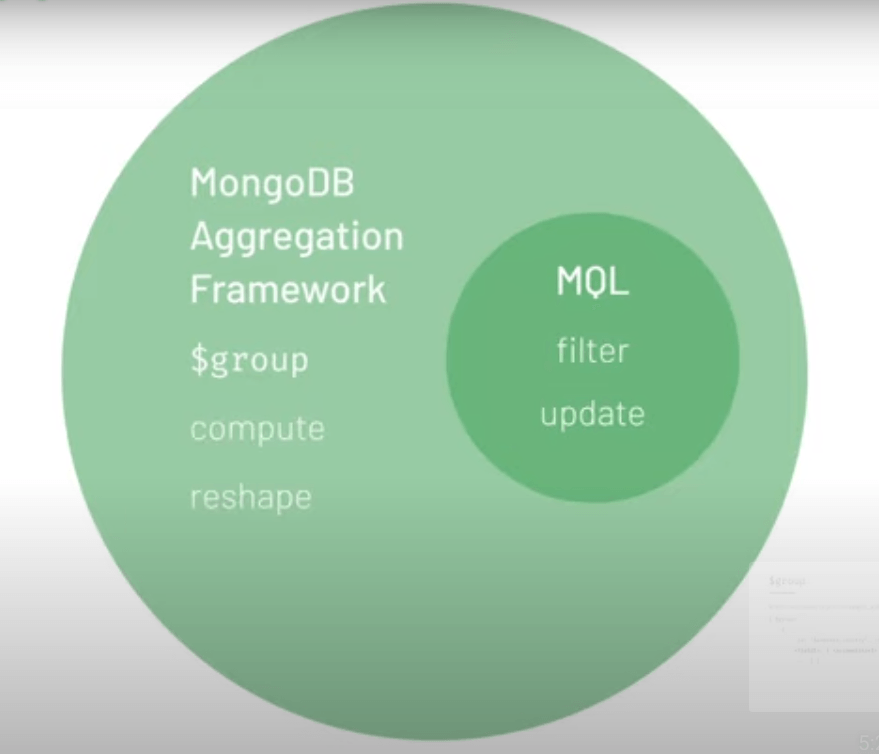
$group

Recap:
sort() and limit()
sort and limit are cursor methods.
A cursor method is not applied to the data in the database, instead applied to the results in the cursor after find command.
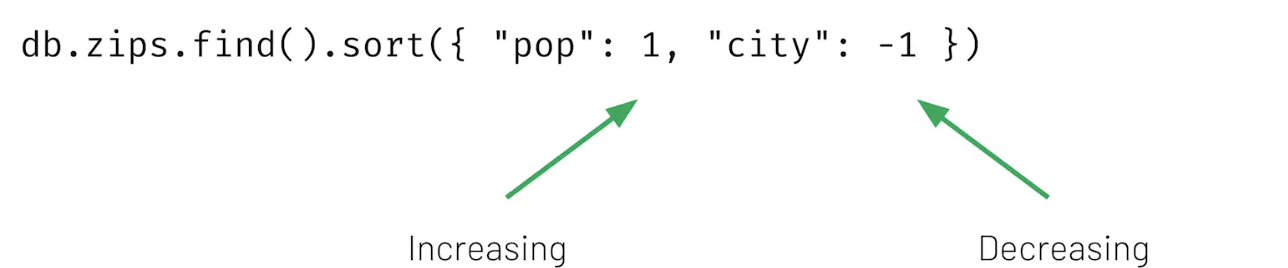
You can sort in increasing or decreasing order:

Introduction to Indexes
Introduction to Data Modeling
Data modeling - a way to organize fields in a document to support your application performance and querying capabilities.
To learn more about data modeling with MongoDB, take our Data Modeling Course! Check out our documentation and blog.

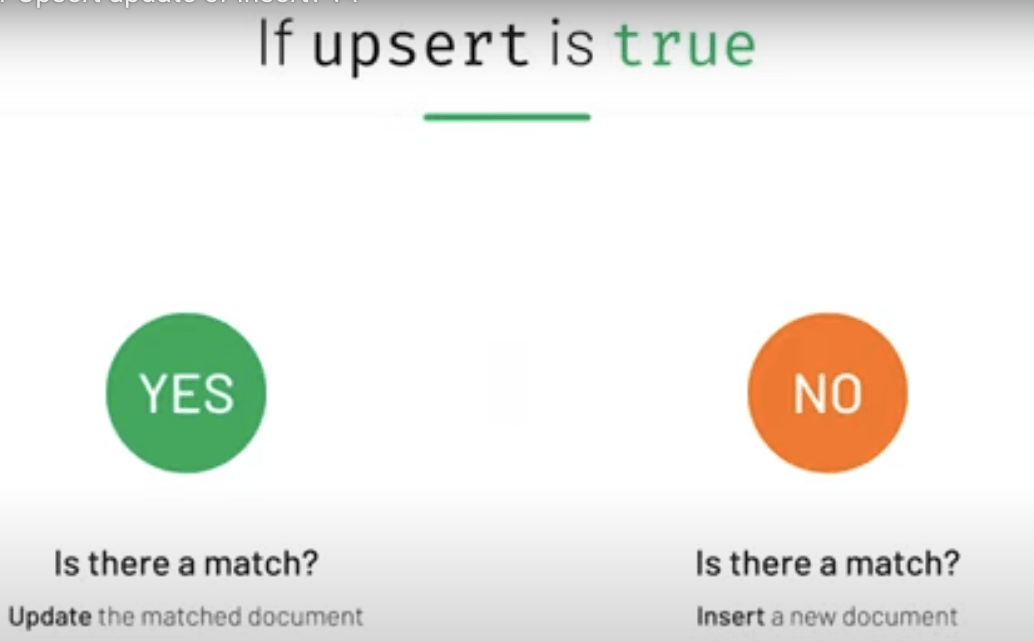
Upsert - Update or Insert?

Aggregation Framework
1. Using the aggregation framework find all documents that have Wifi as one
of the amenities. Only include price and address in the resulting cursor.
2. Which countries have listings in the sample_airbnb database?
3. How many countries have listings in the sample_airbnb database?
sort() and limit()
1. Find the least populated ZIP code in the zips collection.
2. Find the most populated ZIP code in the zips collection.
3. Find the top ten most populated ZIP codes.
4. Get results sorted in increasing order by population, and decreasing
order by city name.
Introduction to Indexes
Create two separate indxes to support the following queries:
db.trips.find({"birth year": 1989})
db.trips.find({"start station id": 476}).sort("birth year": 1)

Documentation about the Validation tab in Compass.
Schema Validation with MongoDB Documentation.
JSON Schema Validation - Locking down your model the smart way.
JSON Schema Validation - Checking Your Arrays
Why MongoDB? (optional)
At this point you have learned enough to start having a meaningful conversation about why developers, DBAs, and companies choose MongoDB as their database.
This can also help you decide whether MongoDB is the right choice for you.
To help you learn more about specific use cases, we put together case studies and articles about some of our customers and community members.
We also added a link to the MongoDB Developer Hub and Community Forums where you can ask questions, learn new things, and connect with others who are diving into MongoDB content and products.
Take a look and feel free to browse for more information.

